Automatic Text Scoring

Aim of the Project
The aim of this project is to develop and end-to-end model which can perform automatic text scoring on essays and to create an user interface which enhances the usage of the model developed.
Intro
Automated Text Scoring (ATS) systems are targeted at both alleviating the workload of the teachers and improving the feedback cycle in educational systems. Traditionally, the task of ATS has been regarded as a machine learning problem which learns to approximate the marking process with supervised learning. This mainly involves trying to extract some handcrafted and standard features of the essays and then passed into a machine learning based classifier. These features were mostly some basic features like essay length, sentence length, grammar correctness, readability etc.
Deep learning based ATS systems demonstrated that neural network architectures such as LSTM and CNN are capable of outperforming systems that extensively required handcrafted features. However, these models do not consider Logical Flow and coherence over time.
In the proposed architecture, SKIPFLOW LSTM adopts parameterized tensor compositions to model the relationships between different points within an essay.
This in turn generates neural coherence features that can support predictions. As said above, it mainly models coherence and semantic relatedness over time. This is done in the following way :
- It reads the essay and models semantic relationships between two points of an essay using Neural Tensor Layer.
- It generates Neural Coherence Features by performing semantic matching k-times while reading.
- It models the relationship between distant states with additional parameters which enhances memorization and improves performance of the deep architecture by allowing access to intermediate states. This eases the burden and provides protection against vanishing gradient by exposing hidden states to deeper layers.
- Most importantly, it performs semantic matching and semantic modeling.
Model Architecture of SKIPFLOW:
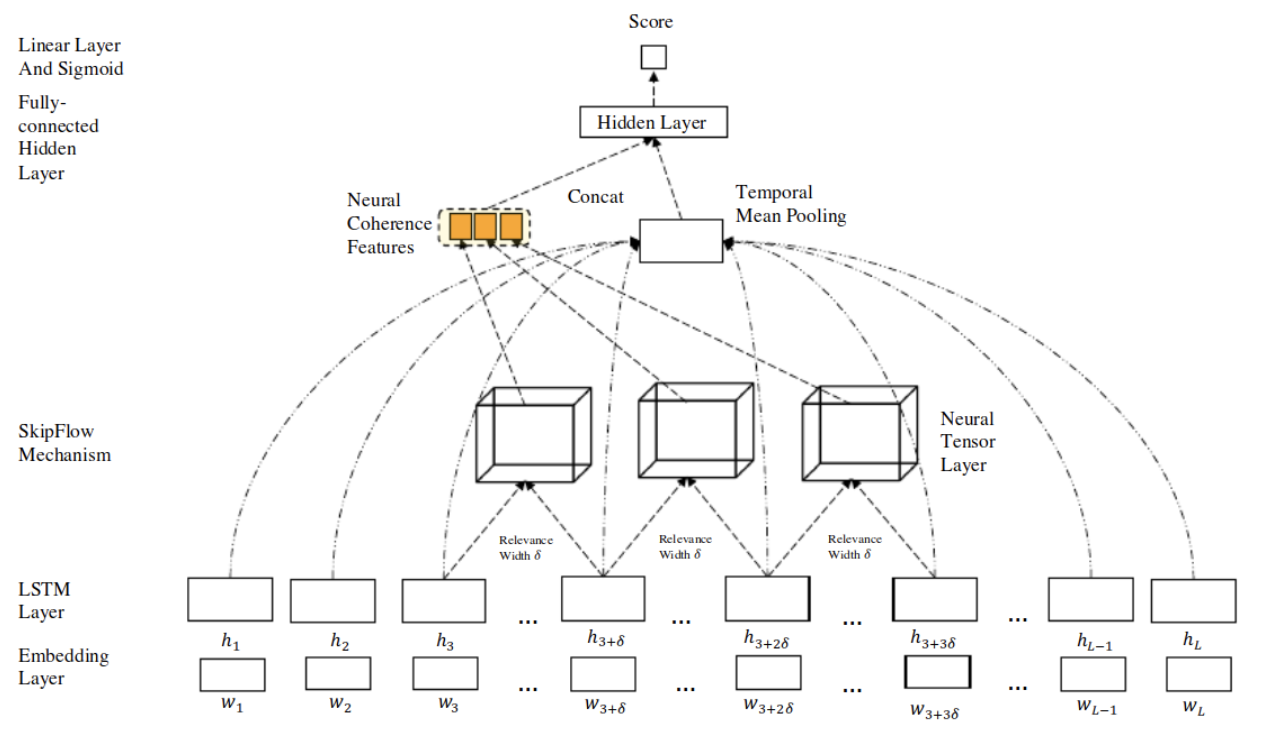
- Embedding layer: The model accepts an easy and the target score as a training instance. And the embedding layer is used to represent each essay as a fixed-length sequence in which we pad all sequences to the maximum length. This helps us obtain word embeddings.
- We have used Glove Embeddings in our Model, instead of a training an embedding layer.
-
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): The sequence of word embeddings obtained from the embedding layer is then passed into a long short-term memory network. At every time step t, LSTM outputs a hidden vector ht that reflects the semantic representation of the essay at position t. And to select the final representation of the essay, a temporal mean pool is applied to all LSTM outputs.
- Neural Tensor Layer: A tensor layer is used to model the relationship between two LSTM outputs. It is a parameterized composition which is defined using :
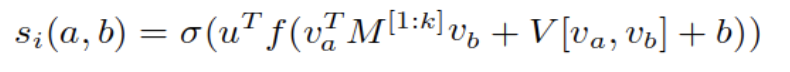
The vector outputs of LSTM at two time steps of δ-width apart are passed through neural tensor layer and it returns a similarity score that determines the coherence feature between the two vectors. The usage of bilinear product enables interaction between vectors through a similarity matrix. This enables a rich interaction between hidden representations. Moreover, the usage of multiple slices(k) encourages different aspects of this relation to be modeled.
- Fully-Connected Hidden Layer: All the scalar values that are obtained from the tensor layer are concatenated together to form the neural coherence feature vector. The essay representation which obtained from a mean pooling over all hidden states is then concatenated with the coherence feature vector. This is then given as an input to the fully connected hidden layer.
- Linear Layer with Sigmoid: This is the final layer. The output at this layer is the normalised score of the essay.
- Learning and Optimization: Network optimizes the mean-squared error.
Tools Used:
- Keras + Tensorflow - for implementing the model and training the model using the ASAP dataset.
- NLTK Toolkit - for preprocessing the data.
- Glove Embeddings - for the embedding layer
Dataset:
We use the ASAP (Automated Student Assessment Prize) dataset from kaggle for experimental evaluation. This dataset contains eight essay sets and each of it has its own unique characteristics. The average length of each essay varies from 150 to 650 words. The statistics of the ASAP dataset are as follows :
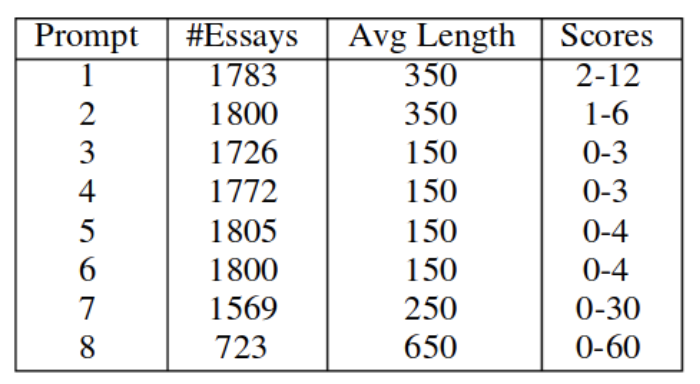
In the above table, the first column represents the type of essay from the eight types. The second column is about the number of essays of each type. The third column gives the information about the average length of essays of that particular type and the last column, scores, denotes the range of possible marks in the dataset.
Evaluation Metric:
Firstly, the experimental setup is a 5-fold cross validation to evaluation all systems with a 60-20-20 split for train, validation and test sets. We trained all models for 1000 epochs or lesser depending on whether the model keeps improving its performance. For word processing, we used tokenizer of NLTK library. The evaluation metric used was the Quadratic Weighted Kappa (QWK) which measures agreement between raters and it is a commonly used metric for ATS systems.
Goals Achieved
- Finished the implementation of the complete end-to-end system.
- Compared the results of the paper with the metrics obtained for the built system.
- Built an interactive demo (web-based) for users to input essays and get the predicted ATS score.
Results
Below are the Kappa Scores Obtained for each essay prompt :
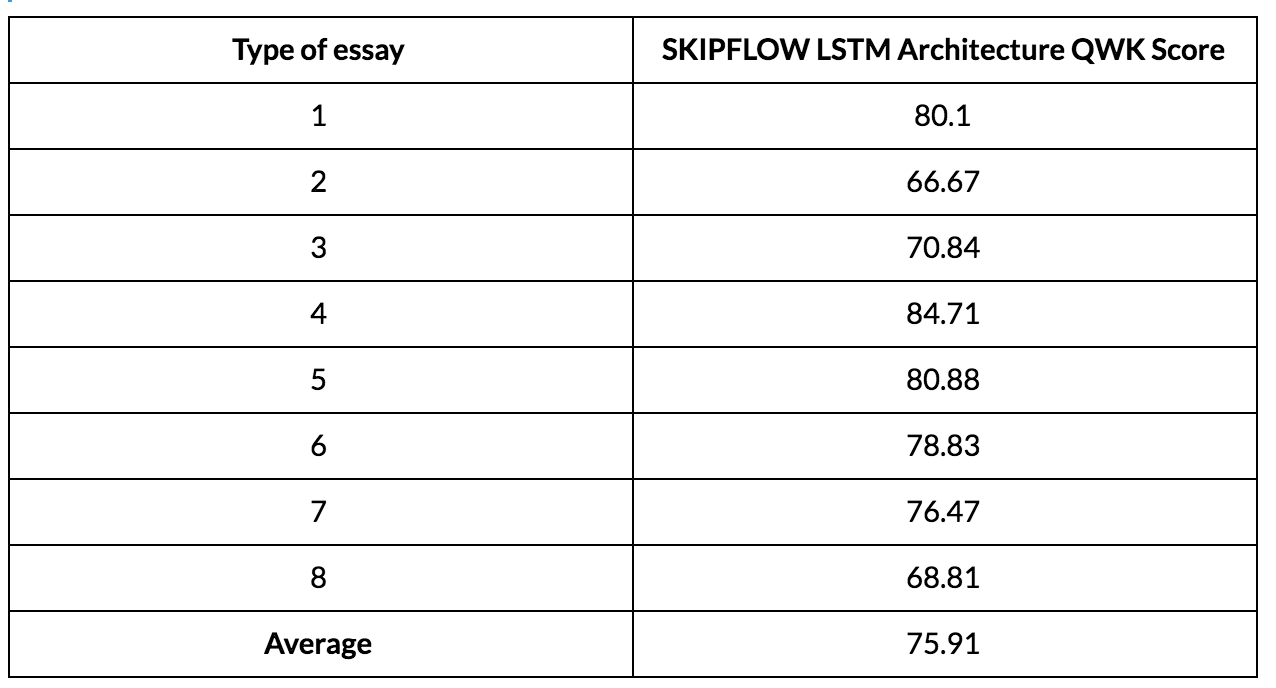
Conclusion:
Thus this system serves the purpose of score prediction for a given essay. This has been mainly done by incorporating the intuition of textual coherence in neural ATS system. SKIPFLOW architecture adopts parameterized tensor compositions to model the relationships between different points within an essay, generating neural coherence features that can support predictions. These neural coherence features when combined with LSTM sentence representations can produces significantly better results.